Kyoto Shogi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 is a modern
is a modern
Shogi Net
Benri Shogi (in Chinese)
{{Shogi variants Board games introduced in 1976 Shogi variants
 is a modern
is a modern variant
Variant may refer to:
In arts and entertainment
* ''Variant'' (magazine), a former British cultural magazine
* Variant cover, an issue of comic books with varying cover art
* ''Variant'' (novel), a novel by Robison Wells
* " The Variant", 2021 e ...
of shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' ...
(Japanese chess). It was invented by Tamiya Katsuya c. 1976.
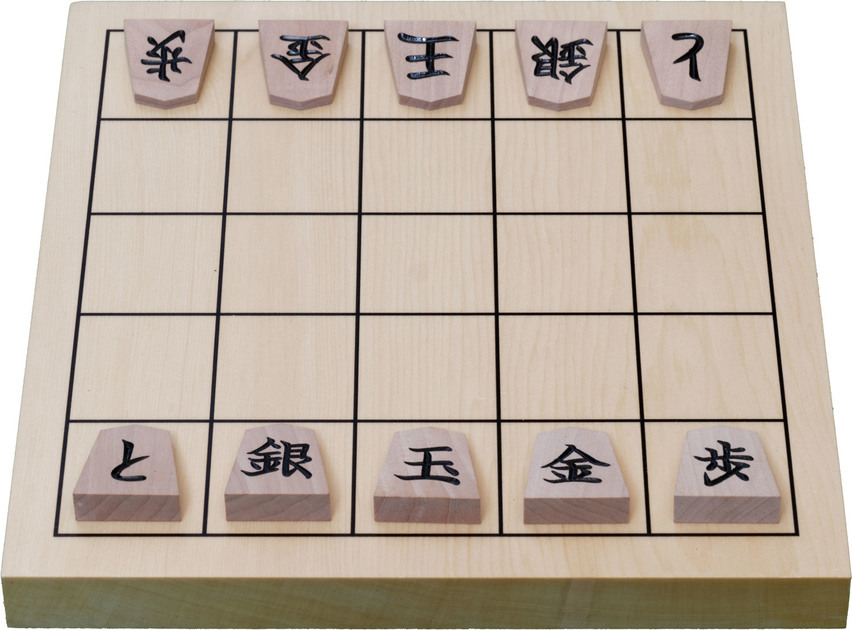
Kyoto shogi is played like standard shogi, but with a reduced number of pieces on a 5×5 board. However, the pieces alternately promote and demote with every move, and the promotion values are entirely different from standard shogi.
Rules of the game
Game equipment
Two players play on a board ruled into a grid of 5 ''ranks'' (rows) by 5 ''files'' (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player has a set of 5 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (most to least powerful) they are: * 1 king * 1 gold general * 1 silver general * 1 tokin * 1 pawn The names of the pieces combine their promoted and unpromoted values, and are puns in Japanese for words with the same pronunciations but different kanji. For example, the lance/tokin is homonymous with the name of the city 京都Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ci ...
, and provides the name of the game.
Setup
Each side places his pieces in the positions shown below, pointing toward the opponent. * In the rank nearest the player: ** The king (K) is placed in the center file. ** The gold general (G) is placed in the adjacent files to the right of the king. ** The silver general (S) is placed in the adjacent files to the left of the king. ** The tokin (T) is placed in the left corner. ** The pawn (P) is placed in the right corner. That is, the first rank is:Promotion
There is no ''promotion zone'' in Kyoto shogi. Every time a piece makes a move it alternately promotes and reverts to its unpromoted state. Promotion is effected by turning the piece over after it moves, revealing the name of its promoted rank; demotion is effected by turning the piece back. The promotion rules and values are reminiscent ofmicroshogi
Microshogi (五分摩訶将棋 ''gofun maka shōgi'' "5-minute (scarlet) poppy chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess), with very different rules for promotion, and demotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOSTNOST (kNights of the Square Table) ...
and entirely different from standard shogi:
* A king cannot promote: K
* A tokin (T) promotes to a lance and ''vice versa:'' T ↔ L
* A silver general promotes to a bishop and ''vice versa:'' S ↔ B
* A gold general promotes to a knight and ''vice versa:'' G ↔ N
* A pawn promotes to a rook and ''vice versa:'' P ↔ R
Movement and capture
A piece is allowed to move, capture or be dropped in a manner that will prevent it from moving on a subsequent turn, which is illegal in standard shogi. For example, a rook can move onto the farthest rank, becoming a pawn and unable to move further. Such pieces may be captured as any other.Drops
A captured piece may be dropped with either side facing up. There are no restrictions on where pieces can be dropped, other than that the square must be empty. So unlike in regular Shogi, pieces can be dropped in places where they can never move again, pawns can be dropped in files that already contain a pawn, and checkmate can be delivered through a pawn drop.Repetition
The original rules states that a third repetition would end the game as a draw, but kept open the possibility that this should be changed if playing experience would reveal it as undesirable. An alternative would be to declare a loss for the player repeating a position too many times, except in cases of perpetual check, where the checker would lose.See also
*Shogi variant
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variant ...
* Whale shogi
Whale Shogi (鯨将棋 ''kujira shōgi)'' is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess). It is not, however, Japanese: it was invented by R. Wayne Schmittberger of the United States in 1981. The game is similar to Judkins shogi, but with more pie ...
* Minishogi
Minishogi (5五将棋 ''gogo shōgi'' "5V chess" or "5×5 chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess). The game was invented (or rediscovered) around 1970 by Shigenobu Kusumoto of Osaka, Japan. The rules are nearly identical to those of ...
* Judkins shogi
Judkins shogi (ジャドケンス将棋 ''Jadokensu shōgi'' "Judkins chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess), however it is not Japanese. Credit for its invention has been given to Paul Judkins of Norwich, UK, prior to April 1998.
...
* Microshogi
Microshogi (五分摩訶将棋 ''gofun maka shōgi'' "5-minute (scarlet) poppy chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess), with very different rules for promotion, and demotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOSTNOST (kNights of the Square Table) ...
* Cannon shogi
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variant ...
* Yari shogi
Yari shogi (槍将棋 ''yari shōgi'', spear chess, where 'spear' is another name for the lance piece) is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess); however, it is not Japanese. It was invented in 1981 by Christian Freeling of the Netherlands. Thi ...
External links
Shogi Net
Benri Shogi (in Chinese)
{{Shogi variants Board games introduced in 1976 Shogi variants